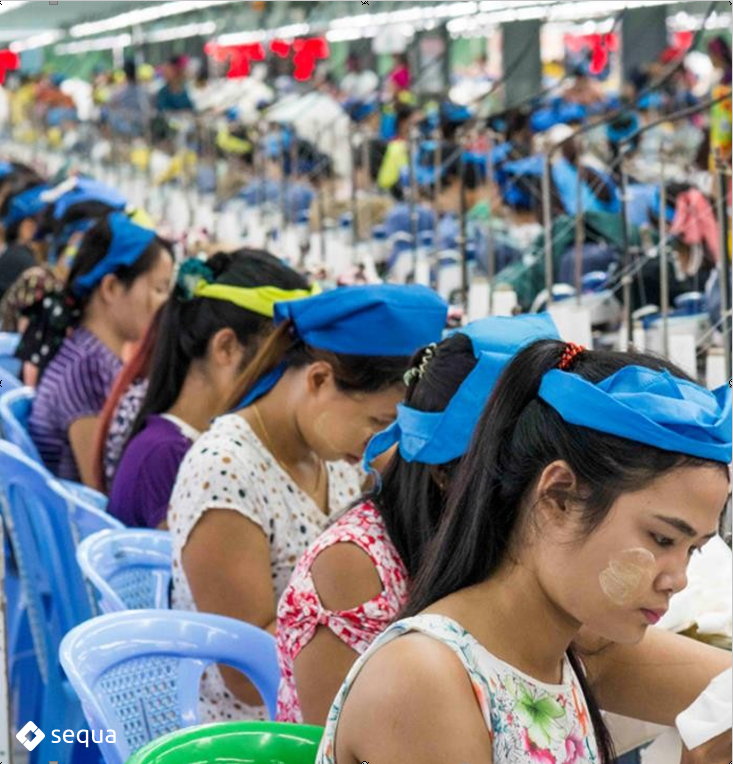
10 million EUR support project for Myanmar garment sector workers in economic crisis during the pandemic
Funded by the European Union, managed by UNOPS, administered directly by local civil society partners and the private sector
160,000 separate monthly cash and food voucher transfers arranged during 2020 and 2021
70,000 direct beneficiaries, 85% women
Telemedicine component for pregnant and lactating mothers on nutrition



1. Research and presentation objectives
1

To assess nutrition knowledge, attitudes and practices among women and their offspring aged less than 2 years at baseline
2
To assess household food insecurity levels at baseline
3

To understand the perceived
impact of the COVID-19
pandemic and political crisis
on households’ income,
livelihoods and food security
2. Methodology
Characteristics of the sample
• Design: pre-post quasi-experimental design
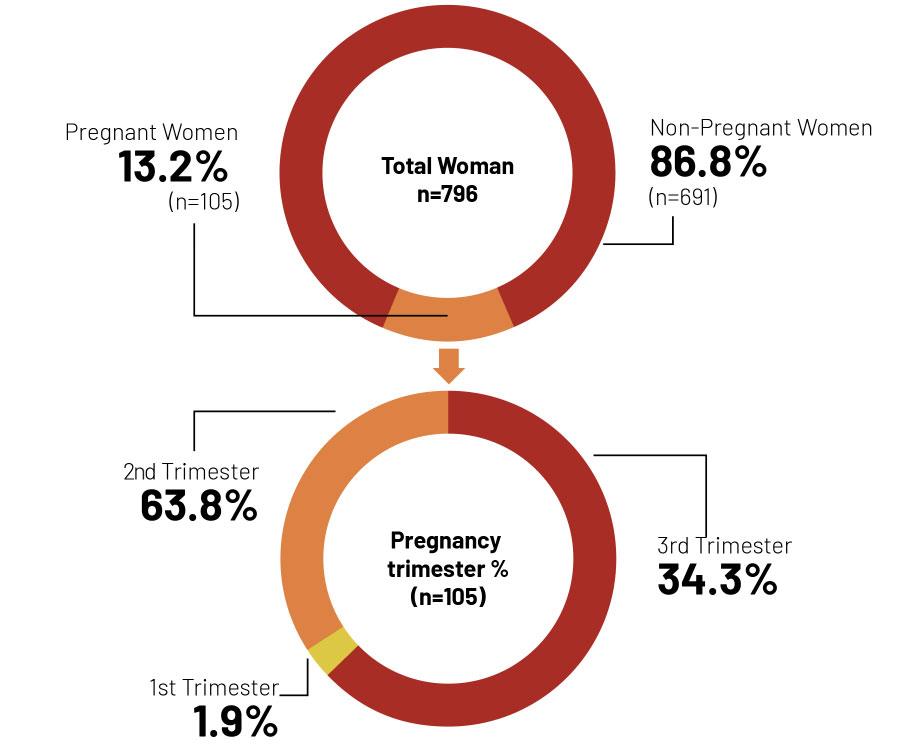
• Sample: Target sample = 800; Analytical sample = 796
• Participants: Female workers (15-49 years old) recipients of the Myan Ku cash transfer and nutrition counselling programme in either 2020 or 2021 that fall into one of the following categories:
1) Pregnant women
2) Lactating women (non-pregnant)
3) Non-pregnant and non-lactating women with a child under 2 years of age
• Setting: Myanmar
• Data collection methods: interviewer-administered questionnaire (via telephone) to collect information on socio-demographic characteristics, the impact of COVID-19 and political instability on livelihoods/food security, maternal and child diet, maternal knowledge/attitudes and household food insecurity

3. Results
Part 1: Descriptive characteristics of the sample
Socio-demographic characteristics
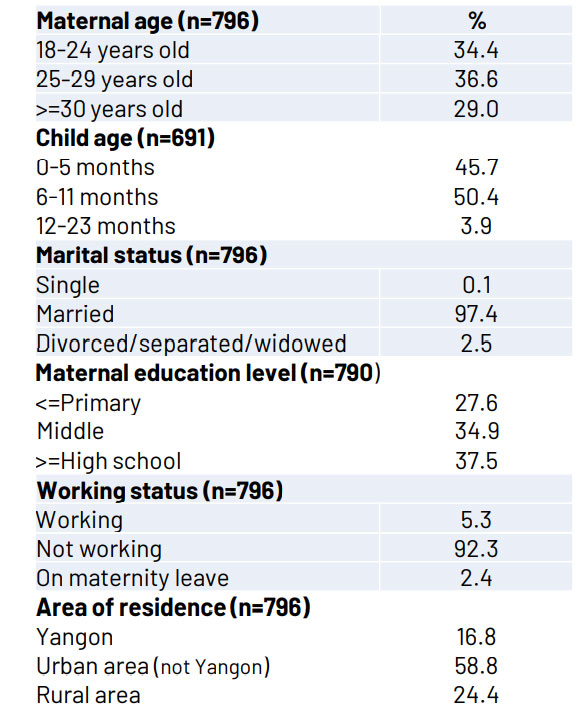
Cash Transfer
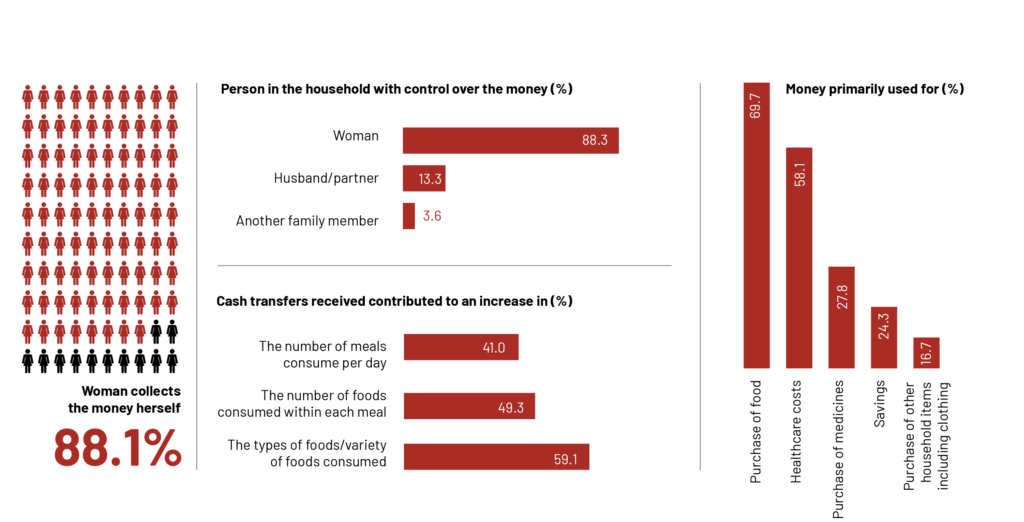
3. Results
Part 2: The impact of the political situation and COVID-19 on income, livelihoods and food security
The impact of the political situation and COVID-19 on income and livelihoods
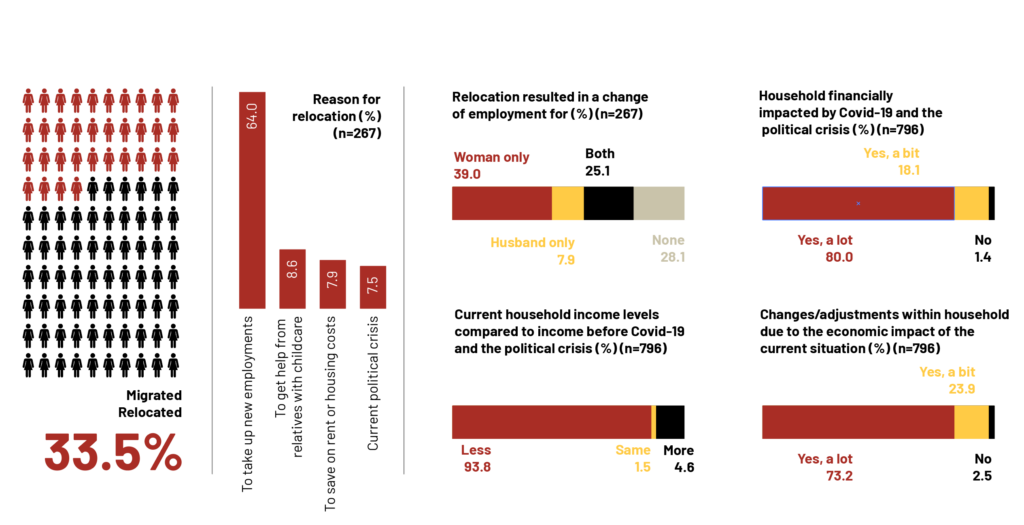
The impact of the political situation and COVID-19 on food security
3. Results
Part 3: Nutrition and food security indicators
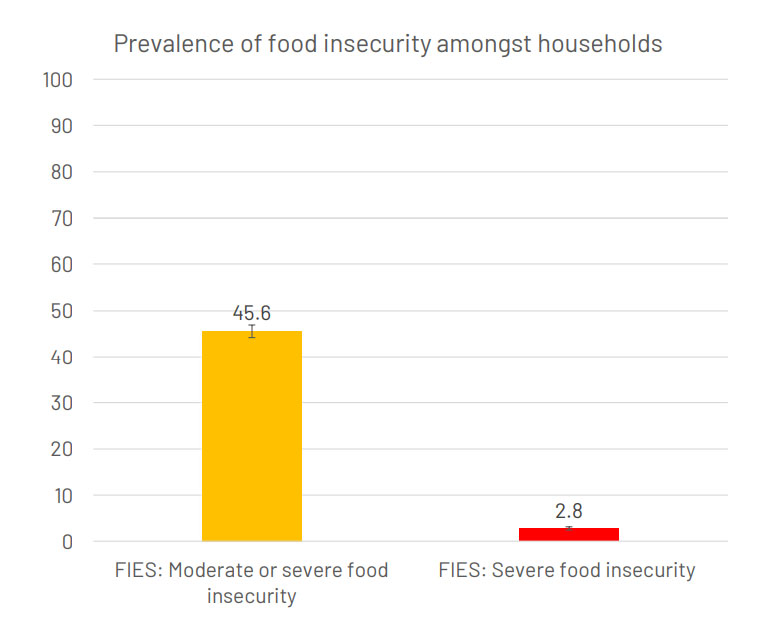
Household indicators (n=779)

Maternal indicators
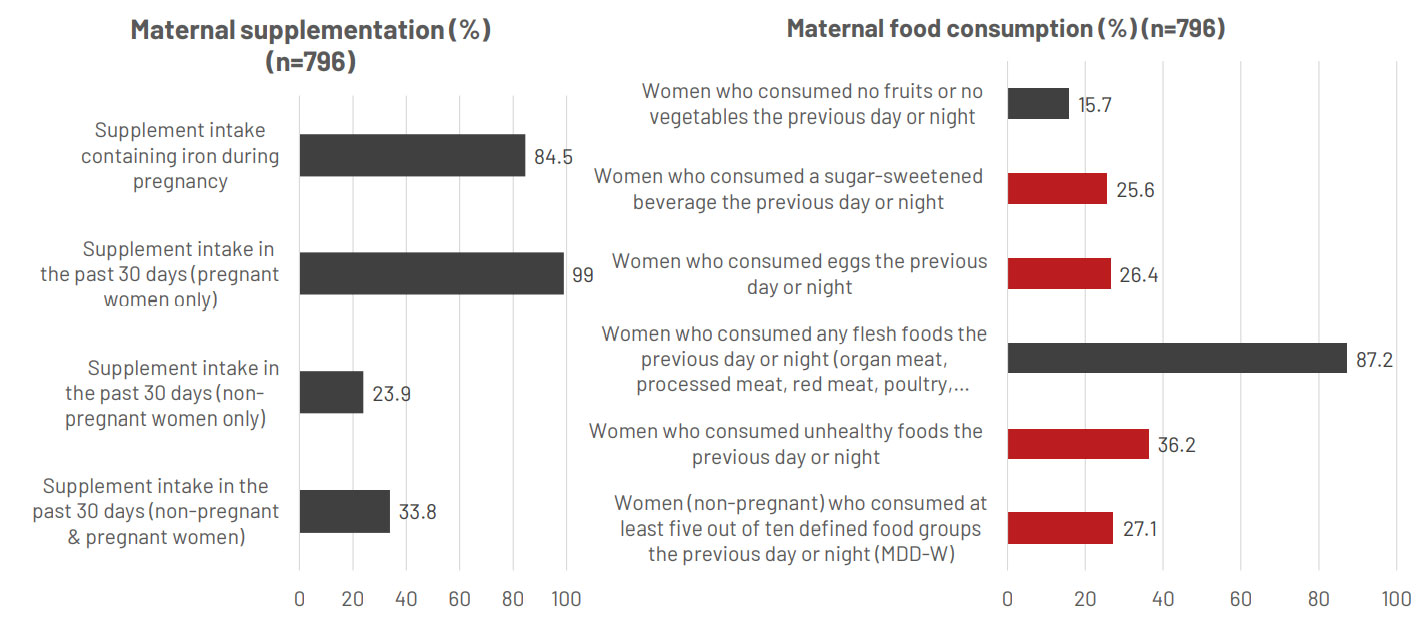
Maternal indicators

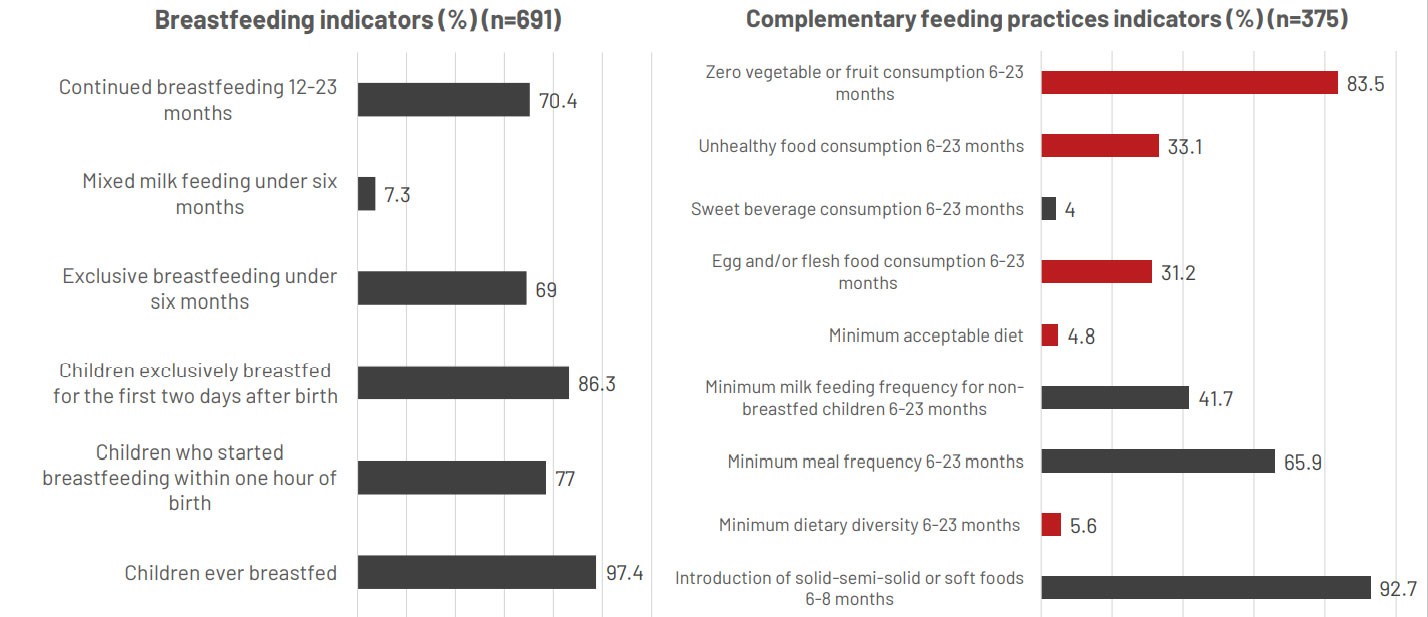
Child indicators
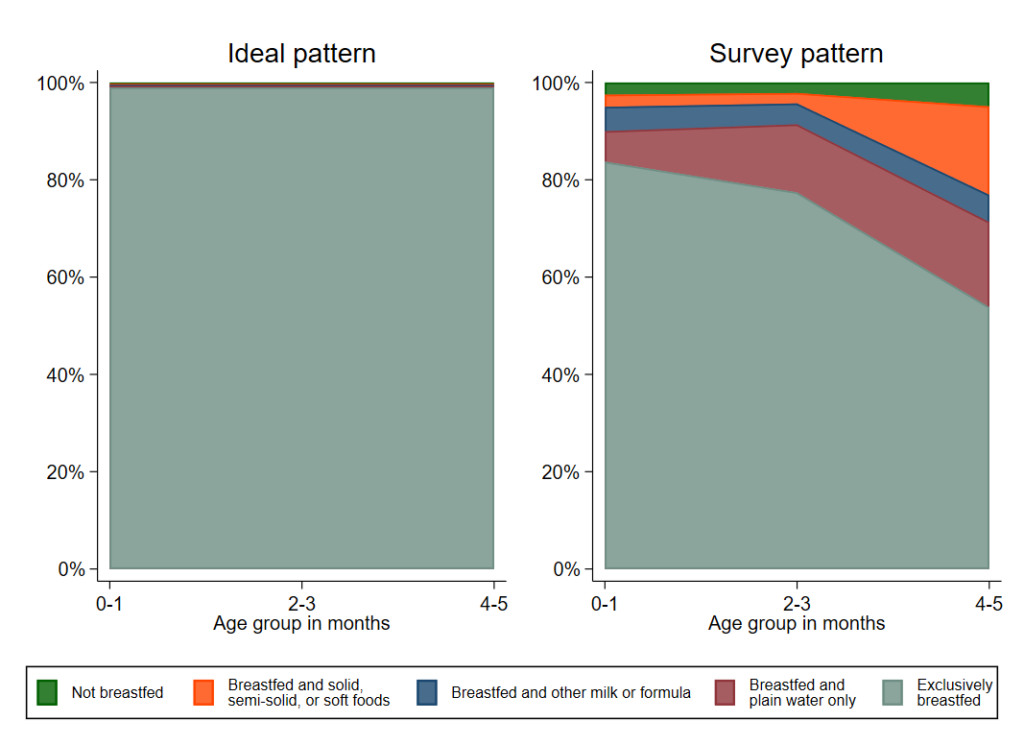
Feeding patterns
Area graph patterns of infant feeding practices by age group (%) (n=316)
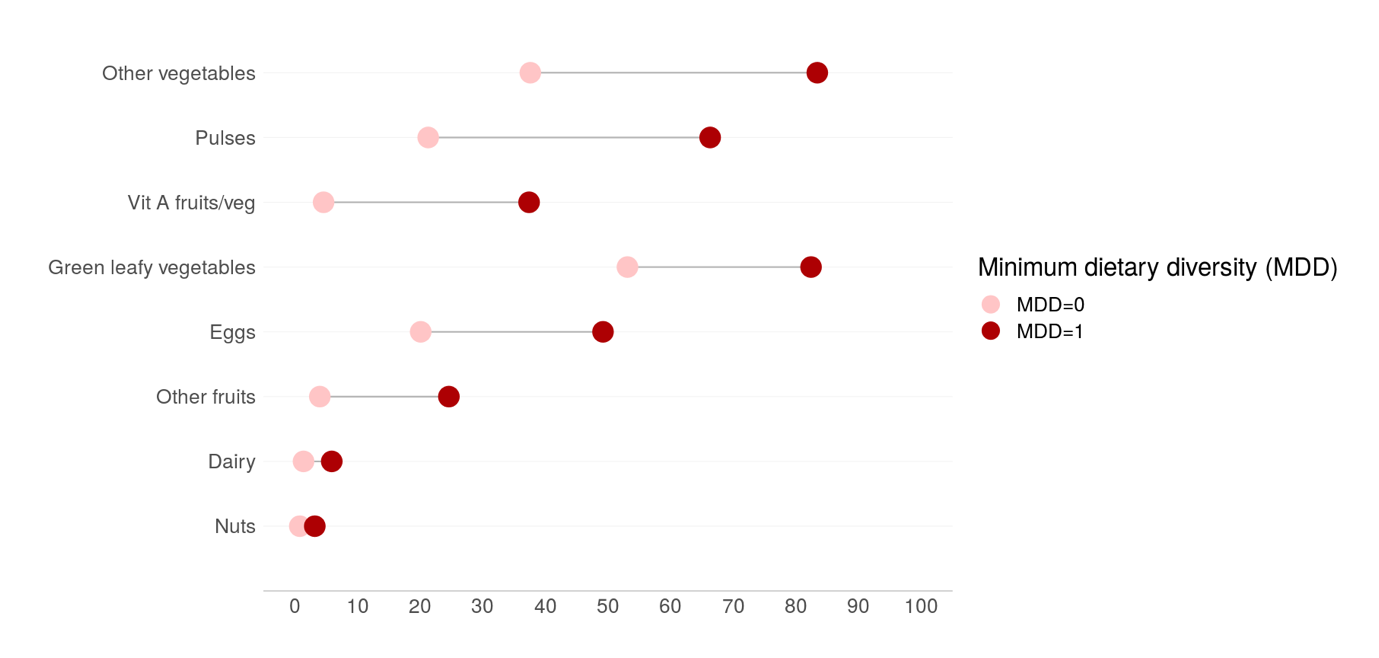
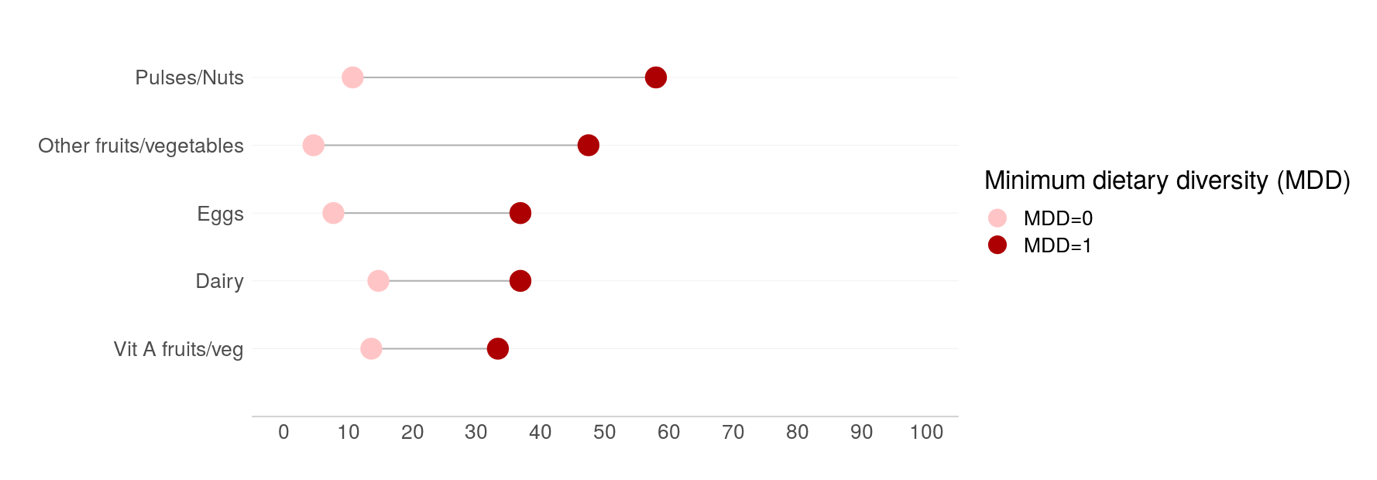
Child food group consumption according to minimum dietary diversity (n=375) (%)
Children meeting minimum dietary diversity (MDD=1) vs children NOT meeting minimum dietary diversity (MDD=0) –
only food groups with significant differences between the two groups
4. Conclusion
Summary of findings
– The majority of women reported that their households’ income and livelihoods have been impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic and political crisis.
– Most women had control over the cash transfer received.
– Cash transfer was primarily used for the purchase of food and it contributed
to an increase in diet quality for themselves and their offspring.
– Despite this, only 3 women out of 10 and 1 child out of 20 ate a diverse diet .
– Food groups to be promoted amongst those not meeting the MDD include:
pulses, dairy, eggs, green leafy vegetables, other vegetables and vitamin A rich fruits and vegetables.
– A very high proportion of infants aged 6-23 months did not consume any fruit or vegetable in the past 24h.
– A relatively high proportion of mothers and their infants consumed
unhealthy foods and beverages